Discover the ultimate guide to understanding, treating, and preventing Sesamoiditis. Dive into expert insights, effective healing strategies, and practical tips to navigate this painful foot condition with confidence.

Introduction
Sesamoiditis, a condition marked by pain beneath the big toe, transforms simple activities into challenging endeavors. This comprehensive guide delves into the heart of Sesamoiditis, exploring its causes, symptoms, and the path to relief. With expert insights and healing strategies, we empower you to step forward into recovery and reclaim the joy of movement.
Table of Contents
What is Sesamoiditis?
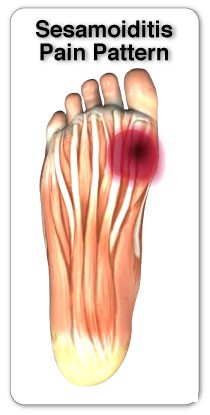
Sesamoiditis is a painful condition affecting the area beneath the big toe, making activities like walking, running, or standing quite uncomfortable. This issue arises from inflammation of the sesamoid bones—two tiny, round bones located in the forefoot beneath the big toe joint. These bones are encased within tendons and serve a critical role in the foot’s mechanics, acting as a fulcrum for tendons to help propel the foot forward during movement. Their strategic position makes them prone to inflammation and injury, resulting in sesamoiditis.
Primary Causes of Sesamoiditis

The root cause of sesamoiditis is often linked to repetitive activities that exert excessive force on the ball of the foot, including:
| High-Impact Sports: Activities such as running, basketball, and soccer, where intense footwork is involved, can place significant stress on the sesamoid bones. |
| Dance: Ballet dancers, in particular, face a high risk due to the frequent pressure applied to the forefoot while dancing on tiptoes. |
| Occupational Hazards: Jobs that require long periods of standing or walking can also contribute to the development of sesamoiditis. |

Factors That Increase the Risk
Several underlying factors can heighten the risk of developing sesamoiditis, making it more likely for some individuals to experience this condition:
Inadequate Footwear: Wearing shoes that do not offer sufficient support or that have high heels can disrupt the natural alignment and pressure distribution of the foot, elevating the risk. Shoes with a tight toe box that squeezes the toes can also contribute to the development of sesamoiditis.
Foot Structure Variations: People with high arches might find that there is an increased force on the ball of the foot, making them more prone to sesamoiditis. Similarly, those with flat feet or other structural abnormalities in the foot may face altered foot mechanics, leading to additional stress on the sesamoid bones.
Existing Foot Conditions: Foot conditions that change how weight is distributed across the foot, such as bunions or hammertoes, can increase the likelihood of sesamoiditis.
Key Symptoms to Be Aware Of
Early detection of sesamoiditis symptoms is crucial for effective treatment and management. Here are the key symptoms to be vigilant about:

Pain in the Big Toe Area
The hallmark symptom of sesamoiditis is a persistent pain under the big toe, particularly in the ball of the foot. This pain may start as mild and worsen over time, becoming more noticeable during activities that put pressure on the forefoot, like walking or running.
Swelling and Bruising
Inflammation around the sesamoid bones can lead to visible swelling or bruising, adding to the discomfort and serving as a physical sign of the condition.
Difficulty with Toe Movement
It may make bending and straightening the big toe difficult or painful, which can affect how you walk and the overall functionality of your foot.
Warmth and Tenderness
A warm feeling or tenderness when touching the area under the big toe can indicate inflammation, helping to distinguish sesamoiditis from other foot issues.
Pain with Specific Footwear or Barefoot Walking
Shoes that lack proper support or have high heels may worsen pain. Likewise, walking barefoot, especially on hard surfaces, can increase discomfort due to insufficient cushioning and support.
Path to Diagnosis and Healing
Sesamoiditis, marked by discomfort beneath the big toe and in the forefoot, demands a meticulous and holistic approach for its diagnosis and management. This article delves into the methods healthcare professionals employ to diagnose this ailment and the effective treatments available to mitigate its symptoms and facilitate recovery.
Diagnosis
The journey to diagnosing sesamoiditis starts with an in-depth evaluation by a healthcare provider, who examines the foot’s anatomy, pinpoints the exact location of the pain, and identifies any activities that worsen the condition. To confirm sesamoiditis and exclude other potential problems like fractures, imaging tests are commonly used, including:
- X-rays: These provide a clear image of the bones to detect any irregularities.
- MRIs: With detailed visuals of both bones and soft tissues, MRIs are instrumental in evaluating the inflammation surrounding the sesamoid bones.
Effective Treatment Strategies
After diagnosing sesamoiditis, the treatment aims to relieve pain, diminish inflammation, and tackle any underlying factors contributing to the condition. Treatment regimens often encompass a mix of the following approaches:
- Rest and Ice: Pausing activities that exert pressure on the foot and applying ice to the affected area can significantly lessen swelling and discomfort.
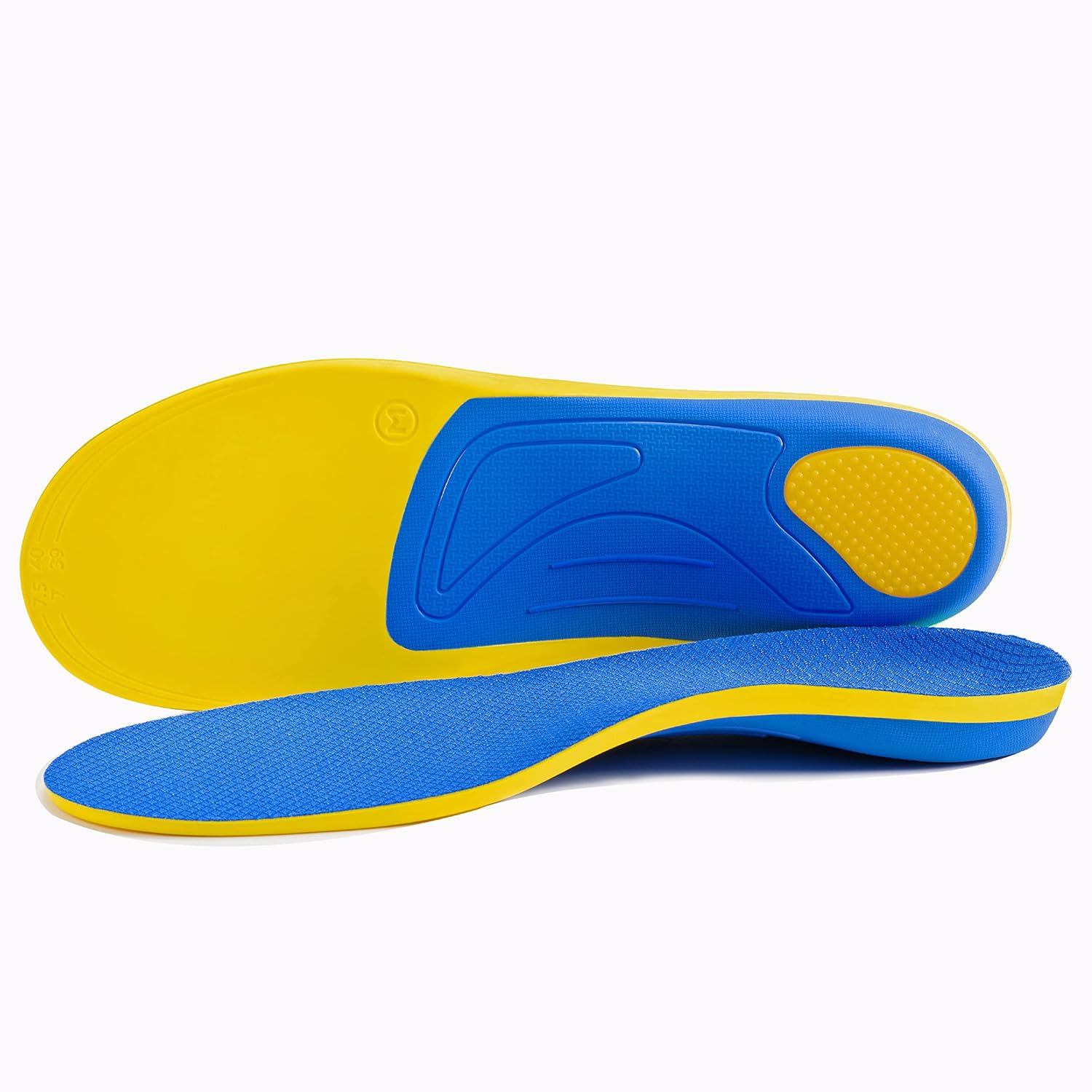
- Cushioned Pads or Orthotic Inserts: These aids can redistribute pressure away from the sesamoid bones, easing pain.
- Supportive Footwear: Opting for shoes with a low heel and a spacious toe box reduces stress on the sesamoid bones. It’s vital to avoid high heels and choose shoes that provide sufficient cushioning and support.
- NSAIDs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are beneficial for pain management and inflammation reduction, offering temporary symptom relief.
- Physical Therapy: Custom exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles around the big toe and enhancing foot mechanics can alleviate pain and prevent future complications.
- Immobilization: In situations where conservative treatments are inadequate, immobilizing the foot with a brace or cast may be necessary for healing.
- Surgery: Surgical intervention might be considered to remove a sesamoid bone or repair damaged tendons if other treatments are unsuccessful.
Prevention Tips
Select Proper Footwear
Preventing sesamoiditis starts with choosing shoes that provide adequate support and comfort, especially for high-impact activities. Avoid shoes with narrow toe spaces that increase stress on the sesamoid bones.
Foot-Strengthening Exercises
Regular exercises that fortify the foot muscles can support arch health and prevent sesamoiditis. Toe curls, marble pickups, and arch lifts are beneficial practices.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Reducing foot pressure and stress starts with keeping a healthy weight, lessening the burden on the sesamoid bones.
Regular Stretching
Enhancing flexibility in the feet, ankles, and calves through stretching can lower the risk of injuries leading to sesamoiditis.
The Importance of Awareness
| Recognizing Symptoms: Prompt detection is key to effective management. Watch out for signs like forefoot pain, swelling, or difficulty moving the toe. |
| Seeking Early Intervention: Consult a healthcare professional if you suspect sesamoiditis or experience ongoing foot pain. Early treatment can halt the condition’s progression and speed up recovery. |
| Educating Yourself and Others: Knowledge about sesamoiditis’s causes, risk factors, and preventive measures empowers you and your community to take proactive foot health steps. |
Moving Forward
Managing sesamoiditis requires patience and commitment to a detailed treatment plan. By following medical advice and incorporating self-care practices, individuals can manage symptoms effectively and journey towards complete recovery. It’s crucial to adhere to your healthcare provider’s guidance and report any symptom changes. With a strategic approach, resuming daily activities free from foot pain is achievable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What exactly is Sesamoiditis?
A: Sesamoiditis is an inflammation of the sesamoid bones located beneath the big toe joint, leading to pain and discomfort in the forefoot.
Q: What causes Sesamoiditis?
A: It’s often caused by repetitive activities that place excessive force on the ball of the foot, such as high-impact sports, dancing, or prolonged standing.
Q: How can I tell if I have Sesamoiditis?
A: Key symptoms include persistent pain under the big toe, swelling, difficulty moving the toe, and tenderness in the area.
Q: What are effective treatments for Sesamoiditis?
A: Treatments range from rest and ice to supportive footwear, orthotic inserts, NSAIDs, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgery.
Q: Can Sesamoiditis be prevented?
A: Yes, by choosing supportive footwear, maintaining a healthy weight, regular stretching, and strengthening foot muscles, you can lower your risk.
Conclusion
Navigating Sesamoiditis requires patience, knowledge, and a proactive approach to treatment and prevention. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms early, and following a comprehensive treatment plan, you can alleviate pain and prevent future occurrences. Remember, your journey to recovery is a step-by-step process. With the right strategies and support, you can move forward confidently, free from the constraints of foot pain.