Constipation is a common condition that affects people of all ages, causing discomfort and affecting daily activities. It’s not just a physical ailment; it can also impact your mental health and quality of life. In this article, we’ll explore essential tips and strategies to overcome constipation, ensuring a smoother and more comfortable daily routine.
Table of Contents
Understanding Constipation
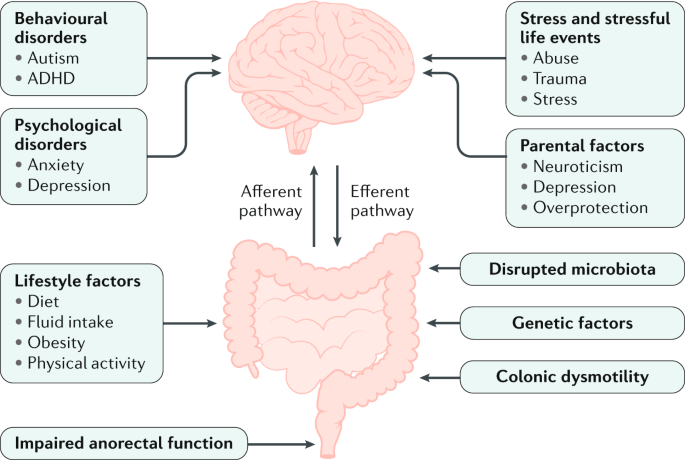
Several factors contribute to the development of constipation, including:
- Dietary Choices: A diet low in fiber is a common cause. Fiber helps to bulk up stools and stimulates the colon to propel contents forward.
- Hydration Levels: Inadequate fluid intake can lead to dehydration, making stools harder and more difficult to pass.
- Physical Activity: A lack of exercise or sedentary lifestyle can decrease bowel motility and lead to constipation.
- Ignoring Bowel Urges: Regularly ignoring the urge to have a bowel movement can lead to constipation. Over time, this can desensitize the body’s natural signals.
- Medications: Some medications, including painkillers, antidepressants, and iron supplements, can cause constipation as a side effect.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and thyroid disorders, can also lead to constipation.
- Psychological Factors: Stress, anxiety, and depression can affect the digestive system and contribute to constipation.
Symptoms of constipation include:
- Having fewer than three bowel movements per week.
- Experiencing hard, dry, or lumpy stools.
- Straining during bowel movements.
- Feeling as though there’s a blockage in your intestines preventing bowel movements.
- Experiencing a feeling of incomplete evacuation after a bowel movement.
It’s important to note that occasional constipation is common and usually not serious. However, chronic constipation can lead to complications such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, or fecal impaction. Understanding the causes and symptoms of constipation is the first step toward finding relief and improving bowel health. Dietary changes, increased physical activity, and adequate hydration are key lifestyle modifications that can help alleviate constipation for many individuals. If symptoms persist, consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable to rule out underlying conditions and to explore other treatment options.

Common Causes
Constipation is a prevalent condition that affects individuals of all ages, and understanding its common causes can help in both prevention and treatment. Here are some of the most frequent reasons people experience constipation:
- Low Fiber Diet: Fiber is essential for softening stools and promoting their easy passage through the digestive system. Diets low in fiber lack the necessary bulk to stimulate bowel movements, leading to constipation. High-fiber foods include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
- Inadequate Hydration: Water and other fluids add moisture to the stool, making it easier to pass. Not drinking enough fluids can lead to dehydration, resulting in hard and dry stools that are difficult to evacuate.
- Lack of Exercise: Physical activity helps stimulate the natural contraction of intestinal muscles, aiding in the movement of stools through the digestive tract. A sedentary lifestyle can decrease this activity, leading to constipation.
- Ignoring the Urge to Go: Regularly ignoring the body’s signals for bowel movements can lead to a diminished response to those signals over time, making constipation more likely.
- Medications: Certain medications can cause constipation as a side effect. These include opioids, some antacids, antidepressants, antiepileptics, and iron supplements, among others.
- Medical Conditions: Several medical conditions can cause or contribute to constipation, including neurological disorders (such as Parkinson’s disease), metabolic and endocrine conditions (like diabetes or hypothyroidism), and gastrointestinal disorders (such as irritable bowel syndrome or IBS).
- Psychological Stress: Stress and mental health issues like anxiety and depression can affect the body in numerous ways, including slowing down digestion, which can lead to constipation.
- Age: Aging can affect bowel regularity due to a decrease in physical activity, changes in diet, and the use of certain medications.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can slow down the digestive system, and the pressure from the growing uterus can further complicate bowel movements.
- Overuse of Laxatives: Ironically, relying too heavily on laxatives can weaken bowel muscles over time, making it more difficult for the body to naturally pass stools.
- Travel or Changes in Routine: Changes in daily routine, such as traveling, can disrupt the body’s normal digestion process and lead to constipation.

Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing the symptoms of constipation is crucial for timely and effective management of the condition. Here are the key symptoms to watch for:
- Infrequent Bowel Movements: One of the most apparent signs of constipation is having fewer than three bowel movements a week. The normal range can vary widely among individuals, but a significant decrease from your usual pattern might indicate constipation.
- Hard, Dry, or Lumpy Stools: Constipation often results in stools that are hard, dry, or lumpy, making them difficult to pass. These stool characteristics are due to prolonged retention in the colon, where water gets absorbed, leaving the stool dry and hard.
- Straining During Bowel Movements: If you find yourself straining or exerting considerable effort to have a bowel movement, it might be a sign of constipation. Straining is not only uncomfortable but can also lead to complications such as hemorrhoids.
- Feeling of Incomplete Evacuation: After a bowel movement, you may feel as though you haven’t fully cleared your bowels. This sensation of incomplete evacuation is a common symptom of constipation.
- Bloating or Abdominal Pain: Constipation can cause bloating and discomfort in the abdomen. In some cases, it can lead to abdominal pain due to the buildup of stool and gas.
- Decreased Appetite: The discomfort and bloating associated with constipation may lead to a decreased appetite in some individuals.
- Nausea: In severe cases, constipation can cause nausea. This symptom typically occurs when there is a significant buildup of stool in the colon.
It’s important to note that experiencing one or more of these symptoms occasionally might not necessarily mean you have a chronic issue with constipation. Diet, activity levels, hydration, and other factors can affect bowel movements on any given day. However, if these symptoms persist, lead to discomfort, or interfere with daily life, it may be indicative of chronic constipation.

Lifestyle Changes for Relief
1. Increase Fiber Intake
Fiber plays a crucial role in adding bulk and moisture to the stool, making it easier to pass. Aim to consume a balanced diet rich in high-fiber foods, such as:
- Fruits: apples, berries, oranges, and pears.
- Vegetables: broccoli, carrots, and leafy greens.
- Whole grains: oatmeal, brown rice, and whole wheat bread.
- Legumes: beans, lentils, and chickpeas. Adults should target at least 25 to 30 grams of fiber per day. However, increase fiber intake gradually to avoid bloating and gas.
2. Stay Hydrated
Drinking sufficient fluids is essential for preventing hard stools. Water is the best choice, but other fluids like herbal teas can also contribute to your daily intake. Aim for at least eight 8-ounce glasses of fluid per day, and consider more if you’re active or live in a hot climate.
3. Regular Exercise
Physical activity helps stimulate intestinal activity, encouraging more regular bowel movements. Incorporate regular exercise into your routine, such as walking, swimming, cycling, or yoga, to help keep your digestive system moving.
4. Establish a Routine
Your body benefits from regularity. Try to establish a consistent time each day for bowel movements, ideally after a meal, to take advantage of the body’s natural rhythms.
5. Mind Your Meals
Eating meals at regular times can help regulate your bowel movements. Avoid skipping meals, and try to have your breakfast, lunch, and dinner around the same time each day.
6. Limit Intake of Irritants
Some foods and drinks can exacerbate constipation for certain individuals. Consider reducing or eliminating caffeine, alcohol, and high-fat foods, which can slow down the digestive process.
7. Manage Stress
Stress can impact your digestive system’s functioning. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga can help manage stress levels and potentially alleviate constipation.
8. Avoid Overuse of Laxatives
While laxatives can provide temporary relief, overuse can lead to dependency and worsen constipation over time. If you need to use a laxative, opt for a gentle, bulk-forming type and consult with a healthcare professional for guidance.
9. Listen to Your Body
Don’t ignore the urge to have a bowel movement. Holding in stool can lead to constipation and other complications. Make it a priority to go when you need to.

Home Remedies That Work
1. Water and Hydration
Increasing your water intake is one of the simplest and most effective remedies for constipation. Dehydration can make stools hard and difficult to pass. Aim for at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water per day, more if you’re active or live in a hot climate.
2. Fiber-Rich Foods
Incorporating more fiber into your diet helps to bulk up stools and makes them easier to pass. Foods high in dietary fiber include fruits (like pears, apples, and berries), vegetables (such as broccoli, carrots, and leafy greens), whole grains, and legumes.
3. Prunes and Prune Juice
Prunes and prune juice are well-known natural remedies for constipation. They are not only high in fiber but also contain sorbitol, a natural laxative that helps soften stools and stimulate bowel movements.
4. Regular Exercise
Physical activity can increase muscle activity in the intestines, helping to move stools through more efficiently. Even a daily walk or light exercise can significantly improve symptoms.
5. Herbal Teas
Certain herbal teas have mild laxative properties that can promote bowel movements. Senna, ginger, and peppermint teas are popular choices for easing digestive discomfort and stimulating digestion.
6. Coffee
For some people, coffee can stimulate the muscles in the digestive system and increase the urge to have a bowel movement. However, caffeine can also be dehydrating, so it’s important to balance coffee consumption with plenty of water.
7. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera juice contains enzymes, vitamins, and minerals that help support overall digestive health. It can act as a natural laxative to encourage bowel movements.
8. Flaxseeds
Flaxseeds are high in fiber and omega-3 fatty acids. Adding ground flaxseeds to your diet can help increase stool bulk and facilitate smoother bowel movements.
9. Probiotics
Probiotics help balance the gut microbiome, improving digestive health and potentially alleviating constipation. They can be found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, or taken as supplements.
10. Warm Lemon Water
Drinking warm water with lemon first thing in the morning can help hydrate the body and stimulate digestion, potentially easing constipation.
11. Castor Oil
Taken in small doses, castor oil can act as a natural laxative. However, it should be used with caution and not become a regular remedy due to potential side effects.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Persistent or Severe Constipation
If constipation lasts for several weeks, is severe, or significantly disrupts your daily life, it’s time to see a doctor. Persistent or severe constipation could indicate an underlying medical condition requiring treatment.
Blood in Stool
Noticing blood in your stool, on toilet paper, or in the toilet bowl can be a sign of a more serious condition, such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, or, in rare cases, colorectal cancer.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Losing weight without trying could indicate a serious health issue, including digestive disorders. If you experience unexplained weight loss along with constipation, it’s crucial to seek medical advice.
Intense Abdominal Pain
Experiencing sharp or persistent abdominal pain alongside constipation may signify blockages, bowel obstructions, or other serious conditions that require immediate medical attention.
Changes in Bowel Movements
Sudden changes in bowel habits, such as consistently narrow stools, could indicate an obstruction or narrowing of the colon. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider if you notice significant changes.
Constipation with Vomiting
If constipation is accompanied by vomiting, it could indicate a bowel obstruction, which is a medical emergency requiring prompt attention.
Failure of Home Remedies
If dietary changes, increased fluid intake, exercise, and over-the-counter treatments do not relieve constipation, a healthcare professional can offer other options and investigate for underlying causes.
Suspected Medication Side Effects
Certain medications can cause constipation. If you suspect a medication is contributing to your symptoms, a healthcare professional can review your prescriptions and suggest alternatives or adjustments.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Individuals with known digestive disorders or other health conditions that could contribute to constipation should consult their doctor if their symptoms worsen or change.
Need for Diagnostic Tests
In some cases, further testing may be necessary to identify the cause of constipation. Your doctor can order tests such as blood tests, a colonoscopy, or imaging studies to get a clearer picture of your digestive health.

Treatment Options
Over-the-Counter Solutions
- Fiber Supplements: Products like psyllium husk, methylcellulose, and polycarbophil can help increase dietary fiber intake, adding bulk to stools and making them easier to pass.
- Stool Softeners: Stool softeners, such as docusate sodium, work by increasing the amount of water the stool absorbs in the gut, making the stool softer and easier to pass.
- Osmotic Laxatives: These draw water into the colon to soften stools and stimulate bowel movements. Examples include polyethylene glycol (PEG) and lactulose.
- Stimulant Laxatives: Stimulant laxatives, such as senna and bisacodyl, increase the rhythmic muscle contractions in the intestines, helping to move stools through the bowel.
- Lubricant Laxatives: Mineral oil is a type of lubricant laxative that coats the stool and keeps moisture within it, allowing for smoother passage through the colon.
Prescription Medications
- Prescription Laxatives: If OTC laxatives are ineffective, stronger versions may be prescribed by a healthcare provider.
- Chloride Channel Activators: Drugs like lubiprostone work by increasing fluid in the intestines to help soften stools and stimulate bowel movements, recommended for certain types of chronic constipation.
- Guanylate Cyclase-C Agonists: Linaclotide and plecanatide are examples that work by increasing fluid secretion in the intestines to make bowel movements easier and are used for chronic constipation.
- Serotonin-5-HT4 Receptor Agonists: Medications such as prucalopride stimulate bowel motility and are prescribed for chronic idiopathic constipation.
Procedural Treatments
In rare cases where medication is not effective or for specific underlying conditions, more invasive treatments may be considered:
- Biofeedback Therapy: For individuals with constipation caused by pelvic floor dysfunction, biofeedback therapy can be effective. This therapy helps patients relearn how to use their pelvic floor and abdominal muscles correctly to facilitate bowel movements.
- Surgery: Surgery may be an option for severe cases of constipation, particularly when there is a structural issue, such as a blockage or rectal prolapse. However, surgery is typically considered a last resort.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies Continuation
Even when using OTC or prescription treatments, continuing with lifestyle adjustments and home remedies is crucial for managing constipation effectively. This includes maintaining a high-fiber diet, staying well-hydrated, engaging in regular physical activity, and not ignoring the urge to have a bowel movement.
Each individual’s response to treatment will vary, so it may take time to find the most effective strategy. It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as needed. Always inform your healthcare provider about any OTC products or home remedies you are using to ensure they do not interfere with prescribed treatments.

FAQs
- How much fiber should I eat per day to prevent constipation?
- Can overuse of laxatives harm me?
- Are there any specific exercises to help with constipation?
- How does stress affect constipation?
- Can certain medications cause constipation?
Conclusion
Constipation can be a frustrating and uncomfortable condition, but with the right strategies and lifestyle changes, it’s manageable. Remember, if symptoms persist or you experience severe discomfort, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional.