Unlock the secrets to diabetic foot care with our comprehensive guide. Discover revolutionary strategies and expert tips to maintain optimal foot health, prevent complications, and empower your mobility. Start your journey to healthier feet today!
Introduction
Welcome to your ultimate guide on mastering diabetic foot care. Living with diabetes means paying extra attention to your foot health to prevent complications that can arise from neuropathy and poor circulation. This guide is designed to empower you with proven strategies, expert tips, and innovative solutions to keep your feet healthy, comfortable, and free from infections or ulcers. Whether you’re newly diagnosed or looking to enhance your foot care routine, you’ll find invaluable insights to protect your feet and maintain your quality of life.
Table of Contents
Understanding Diabetic Foot

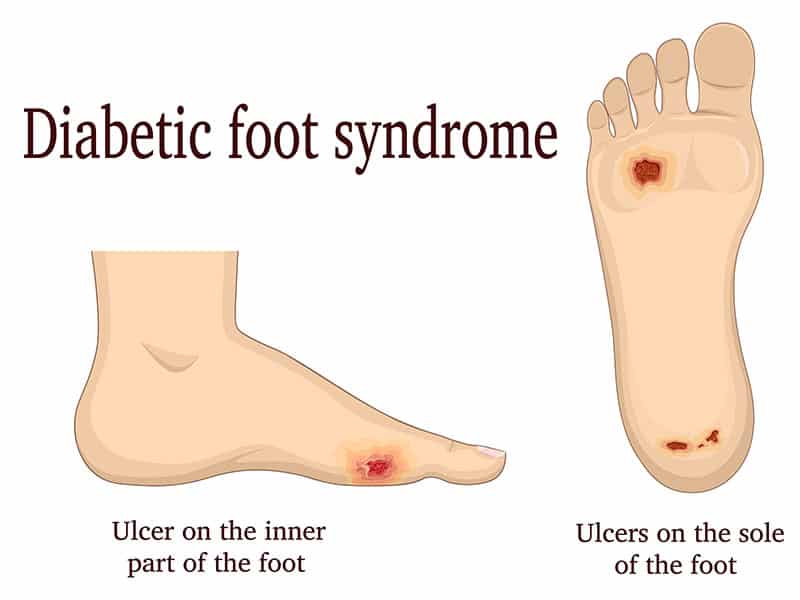
Diabetic foot encompasses a variety of foot-related complications that can arise in individuals with diabetes, primarily due to neuropathy (nerve damage) and impaired circulation. These conditions make the feet particularly vulnerable to injuries, infections, and other serious complications. Understanding the underlying causes, recognizing early symptoms, and adopting comprehensive prevention strategies are crucial for effective management of diabetic foot, ensuring the preservation of foot health.
Causes of Diabetic Foot
Neuropathy (Nerve Damage)
Over time, elevated blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can lead to significant nerve damage, known as neuropathy. This condition often results in a diminished ability to feel pain, heat, or cold, leaving individuals unaware of injuries, blisters, or infections on their feet. The absence of sensation increases the risk of unnoticed injuries becoming more severe, complicating treatment and recovery.
Poor Circulation
Diabetes can also compromise blood flow, particularly to the extremities, such as the feet. This impaired circulation can slow the healing process for cuts, sores, or any wounds, significantly elevating the risk of infection or the development of ulcers. Reduced blood flow can also contribute to heart and blood vessel diseases, further complicating the health of someone with diabetes.
Symptoms to Watch For
Loss of Sensation
A notable reduction in sensation or complete numbness in the feet or toes is often an early indicator of diabetic foot, signaling potential nerve damage.
Tingling Sensations or Pain
Experiencing tingling, burning, or sharp pains in the feet may suggest neuropathy, indicating that nerve damage has occurred.
Skin Color Changes
Noticing changes in the skin color of the feet, such as shifts to red, blue, or pale hues, can be a warning sign of circulation issues.
Swelling
Any swelling in the feet or ankles could point to underlying complications related to diabetic foot and should be monitored closely.

Non-healing Sores or Ulcers
The presence of sores, blisters, or ulcers on the feet that do not heal within a reasonable timeframe is a critical concern, as it increases the risk of severe infections.
Signs of Infection
Warmth, redness, swelling, or discharge from a wound on the foot are indicative of an infection, necessitating immediate medical intervention.
The Crucial Role of Routine Foot Examinations for Diabetics
Routine foot examinations are a cornerstone in the proactive management and early identification of diabetic foot complications, playing a vital role in averting severe outcomes like ulcers, infections, and the risk of amputation. For individuals living with diabetes, engaging in both self-conducted examinations at home and professional evaluations is indispensable, profoundly influencing their foot health and overall well-being.
In-depth Self-Examination Practices
For those with diabetes, incorporating foot self-examinations into their daily regimen is essential for early problem detection and ease of treatment. Detailed self-examination involves:
Daily Visual and Physical Inspections:
- Visual Checks: Daily inspect your feet for abnormalities such as cuts, sores, blisters, redness, calluses, or ingrown toenails. Employ a mirror to view the soles or seek assistance if visibility is an issue.
- Physical Sensation Checks: Feel your feet for any irregularities like lumps, bumps, or swelling. Assess any temperature variations between your feet as this may signal circulatory problems.
- Observation for Changes: Be vigilant about any alterations in the color or shape of your feet, indicative of potential issues.
- Sensation Monitoring: Stay alert to any new pain, tingling, numbness, or sensations, which could signify neuropathy or circulatory challenges.
Professional Examination Necessities
While self-checks are critical, professional evaluations offer a comprehensive safeguard. These examinations, recommended annually or more as per medical advice, include:
Detailed Foot Inspection:
- A healthcare professional will conduct an exhaustive inspection for signs similar to those in self-examinations, utilizing their expertise to identify less obvious issues.
Neurological Testing:
- Evaluations to assess foot nerve health, often employing a monofilament test to gauge touch sensitivity.
Circulatory Evaluation:
- Examination of blood flow to the feet to identify any circulatory deficiencies.
Dermatological and Nail Care:
- Professional handling of calluses, corns, and toenail care to avert complications that might arise from self-treatment.
Footwear Consultation:
- Recommendations on appropriate footwear and socks to prevent the development of pressure sores and blisters.
The Importance of Early Intervention
The essence of regular foot examinations lies in the timely detection and intervention of diabetic foot complications. Early identification and management of minor issues can prevent their escalation into severe conditions, safeguarding the health of your feet. Through vigilant monitoring and maintenance, it’s possible to avoid infections, ulcers, and the subsequent need for more drastic medical interventions such as hospitalization or surgery. This proactive approach not only preserves foot health but also significantly enhances the quality of life for individuals with diabetes, underscoring the importance of routine foot care in diabetes management.
Advancements in Diabetic Foot Complication Management

Recent years have witnessed remarkable progress in the treatment and management of diabetic foot complications, with new technologies and methodologies enhancing patient care. These innovations span from sophisticated wound care products and surgical techniques to the adoption of personalized orthotic solutions and lifestyle adjustments, forming a holistic approach to combatting diabetic foot issues.
Sophisticated Wound Care Innovations
Enhanced Wound Dressings:
Modern dressings now incorporate substances like silver or honey, known for their antimicrobial properties, to expedite healing and mitigate infection risks.
Growth Factor Therapy:
This cutting-edge treatment applies growth factors—key proteins in tissue repair—directly to wounds, significantly boosting the healing process.
Bioengineered Skin Substitutes:
For covering extensive ulcers, these substitutes offer a breakthrough solution, acting as a scaffold for tissue regeneration and accelerating wound closure.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT):
NPWT, or vacuum-assisted closure, employs suction technology to remove wound exudate and enhance blood circulation to the wound site, fostering faster healing.
Surgical Innovations for Diabetic Foot
In critical cases, surgical interventions become indispensable:
Debridement:
This procedure involves the surgical removal of necrotic or infected tissue, thereby improving the healing environment for the healthy tissue.
Revascularization Techniques:
Surgical procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery are employed to restore blood flow to ischemic areas, essential for patients with compromised circulation.
Amputation:
While considered a last resort, partial or total amputation may be necessary for the most severe cases. The focus, however, remains on prevention through early and aggressive treatment strategies.
Personalized Orthotic Solutions and Protective Footwear
Custom-designed orthotics are instrumental in distributing pressure evenly across the foot, preventing ulcer formation in high-risk areas. These devices, tailored to each patient’s foot anatomy, along with specialized diabetic shoes, offer significant protection against foot injuries and enhance patient comfort.
Comprehensive Lifestyle and Dietary Interventions
Lifestyle and dietary adjustments form the cornerstone of diabetes and diabetic foot complication management:
Encouraging Regular Physical Activity:
Exercise not only aids in blood sugar control but also promotes better circulation, reducing the risks associated with neuropathy and vascular issues.
Adopting a Nutrient-Rich Diet:
A balanced diet, emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, supports effective blood sugar management. Limiting saturated fats and refined sugars is also crucial for vascular health.
Smoking Cessation:
Given smoking’s adverse effects on circulation, quitting is imperative for individuals with diabetes to facilitate wound healing and reduce complication risks.
Rigorous Blood Sugar Control:
Maintaining blood glucose levels within recommended ranges is vital to prevent the myriad complications of diabetes, including foot problems.
Footwear Guidance for Diabetics: Ensuring Foot Safety

For those managing diabetes, selecting appropriate footwear transcends mere fashion or comfort—it’s a critical component of their healthcare regimen. Inadequate footwear can precipitate blisters, sores, and ulcers, which pose a heightened risk of severe infections due to the diabetes-related complications of reduced blood flow and neuropathy. Below are detailed footwear recommendations for individuals with diabetes to safeguard their feet, thereby preserving their mobility and enhancing their life quality.
1. Prioritizing Proper Fit
Professional Measurements: Given that foot dimensions and shape may evolve, particularly in the context of diabetes, it’s advisable to have your feet professionally measured to ascertain the correct shoe size.
Consideration for Swelling: Recognizing that feet tend to swell throughout the day, it’s best to try on new shoes during the late afternoon or evening when your feet have expanded to their maximum size.
Adequate Width is Crucial: Ensure the shoes provide sufficient width to avoid constricting pressure points that could lead to blisters and calluses.
2. Seeking Supportive Attributes
Essential Arch Support: Shoes with adequate arch support help in evenly distributing foot pressure, mitigating the risk of discomfort and injuries.
Necessary Cushioning: Opt for footwear that incorporates cushioning to absorb shocks and safeguard your feet.
Adjustable Fit: Prefer shoes with adjustable features such as laces, buckles, or Velcro straps, allowing for a customized fit that can accommodate fluctuations in foot volume.
3. Choosing Breathable Materials
Select Breathable Footwear: Shoes crafted from leather, canvas, or other breathable fabrics can aid in maintaining dry feet, thus lowering the risk of fungal infections.
Moisture-wicking Features: Footwear with moisture-wicking linings is beneficial in keeping feet dry by drawing away sweat.
4. Ensuring Interior Comfort
Smooth or Seamless Inside: Select shoes with minimal internal seams or those lined with soft materials to prevent friction against the skin, which could lead to blisters or sores.
5. Exploring Diabetic-specific Footwear and Orthotics
Diabetic Footwear: Specially designed shoes for diabetics aim to minimize skin breakdown risks by offering additional depth for orthotic accommodation.
Personalized Orthotics: Healthcare providers can prescribe custom orthotics to address specific foot conditions, ensuring even pressure distribution and averting complications.
6. Diligent Footwear Maintenance and Replacement
Routine Inspections: Regularly examine your shoes for signs of deterioration, such as interior wear, holes, or diminishing sole integrity, which could cause foot irritation.
Timely Replacement: Replace shoes before they become overly worn to maintain the protective and supportive benefits essential for diabetic foot care.
7. The Importance of Foot Protection
Continuous Footwear Use: To prevent injuries, it’s crucial to wear shoes or slippers consistently, even indoors, to shield your feet from potential harm.
FAQ Section
Q1: Why is foot care so important for people with diabetes? A1: Foot care is crucial for individuals with diabetes due to the higher risk of foot complications like ulcers, infections, and neuropathy caused by high blood sugar levels. Proper foot care helps prevent these issues and maintains overall foot health.
Q2: What are the signs of diabetic foot complications? A2: Key signs include loss of sensation, tingling or pain, changes in skin color, swelling, non-healing sores or ulcers, and signs of infection. Early detection of these symptoms is vital for effective management.
Q3: How often should I inspect my feet? A3: Daily foot inspections are recommended to identify potential problems early. Look for any changes or injuries, and consult a healthcare provider if you notice anything unusual.
Q4: What type of footwear should people with diabetes wear? A4: Choose shoes that fit well, offer good support, and are made from breathable materials. Consider diabetic-specific footwear and custom orthotics to reduce pressure points and prevent complications.
Q5: Can lifestyle changes impact diabetic foot health? A5: Yes, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, and controlling blood sugar levels play a significant role in preventing diabetic foot complications.
Conclusion
Mastering diabetic foot care is a journey that requires awareness, diligence, and proactive management. By incorporating the strategies outlined in this guide, you can significantly reduce the risk of foot complications, enhance your mobility, and improve your quality of life. Remember, the key to healthy feet lies in routine care, wearing the right footwear, and seeking professional advice when necessary. Empower your steps with the knowledge and tools to protect your feet, ensuring a happier, more active life despite diabetes.